K8S学习笔记
# minikube
https://minikube.sigs.k8s.io/docs/start/ (opens new window)
# Installation
curl -LO https://storage.googleapis.com/minikube/releases/latest/minikube-latest.x86_64.rpm
sudo rpm -Uvh minikube-latest.x86_64.rpm
2
# Start your cluster
useradd k8s
usermod -a -G docker k8s
passwd
su - k8s
# 启动集群
minikube start
# 启动集群
minikube start \
--driver=docker \
--kubernetes-version=v1.23.8 \
--image-mirror-country='cn' \
--image-repository='registry.cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com/google_containers' \
--extra-config=apiserver.service-node-port-range=30000-65535
# 停止集群
minikube stop
# 获取集群状态
minikube status
# 删除集群
minikube delete
# 查看集群IP
minikube ip
# 查看集群日志
minikube logs
# 打印minikube版本信息
minikube version
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
# Interact with your cluster
minikube kubectl -- get pods -A
# 修改.bashrc,添加 alias kubectl="minikube kubectl --"
vim .bashrc
# 刷新.bashrc
source .bashrc
# 可以使用 kubectl 代替 minikube kubectl
kubectl get po -A
2
3
4
5
6
# Deploy applications
Create a sample deployment and expose it on port 80:
kubectl create deployment hello-minikube --image=docker.io/nginx:1.23
kubectl expose deployment hello-minikube --type=NodePort --port=80
2
It may take a moment, but your deployment will soon show up when you run:
[k8s@k8s ~]$ minikube service hello-minikube
|-----------|----------------|-------------|---------------------------|
| NAMESPACE | NAME | TARGET PORT | URL |
|-----------|----------------|-------------|---------------------------|
| default | hello-minikube | 80 | http://192.168.49.2:30831 |
|-----------|----------------|-------------|---------------------------|
🎉 Opening service default/hello-minikube in default browser...
👉 http://192.168.49.2:30831
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
The easiest way to access this service is to let minikube launch a web browser for you:
[k8s@k8s ~]$ minikube service hello-minikube
|-----------|----------------|-------------|---------------------------|
| NAMESPACE | NAME | TARGET PORT | URL |
|-----------|----------------|-------------|---------------------------|
| default | hello-minikube | 80 | http://192.168.49.2:30831 |
|-----------|----------------|-------------|---------------------------|
🎉 Opening service default/hello-minikube in default browser...
👉 http://192.168.49.2:30831
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
Alternatively, use kubectl to forward the port:
kubectl port-forward service/hello-minikube --address 0.0.0.0 8080:80
Tada! Your application is now available at http://localhost:8080/.
# Dashboard
部署和访问 Kubernetes 仪表板(Dashboard) (opens new window)
1、默认情况下不会部署 Dashboard。可以通过以下命令部署:
kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kubernetes/dashboard/v2.6.1/aio/deploy/recommended.yaml
cd /home/k8s
wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kubernetes/dashboard/v2.6.1/aio/deploy/recommended.yaml
mv recommended.yaml kubernetes-dashboard-v2.6.1.yaml
kubectl apply -f /home/k8s/kubernetes-dashboard-v2.6.1.yaml
kubectl delete -f /home/k8s/kubernetes-dashboard-v2.6.1.yaml
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
2、为 Dashboard 添加外网访问:
kubectl port-forward -n kubernetes-dashboard --address 0.0.0.0 service/kubernetes-dashboard 8001:443
访问 https://192.168.1.26:8001/ 即可
3、获取需要登录的token
kubectl get secret $(kubectl get serviceaccount dashboard -o jsonpath="{.secrets[0].name}") -o jsonpath="{.data.token}" | base64 --decode
如果没有token,那就创建一个
kubectl create serviceaccount dashboard -n default
kubectl create clusterrolebinding dashboard-admin -n default --clusterrole=cluster-admin --serviceaccount=default:dashboard
2
error: listen tcp 127.0.0.1:8001: bind: address already in use
# 找到被占用的端口,以8001为例
[k8s@k8s ~]$ netstat -tulpn | grep 8001
(Not all processes could be identified, non-owned process info
will not be shown, you would have to be root to see it all.)
tcp6 0 0 :::8001 :::* LISTEN 9471/kubectl
# 释放对应的端口,9471为对应的PID
kill -9 9471
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
# Concepts
https://kubernetes.io/docs/home/ (opens new window)
资源创建方式有两种:
- 命令行
- YAML
# kubectl
kubectl 命令行的语法格式如下:
kubectl --help
kubectl [command] [TYPE] [NAME] [flags]
2
command:子命令,用于操作 k8s 集群资源对象的命令,例如 create、get、describe、delete。
更多命令见:https://kubernetes.io/docs/reference/generated/kubectl/kubectl-commands (opens new window)
TYPE:k8s 集群中资源对象的类型,区分大小写,能以单数、复数或者简写形式表示
pod(po)
service(svc)
replication controller(rc)
deployment(deploy)
replica set(rs)
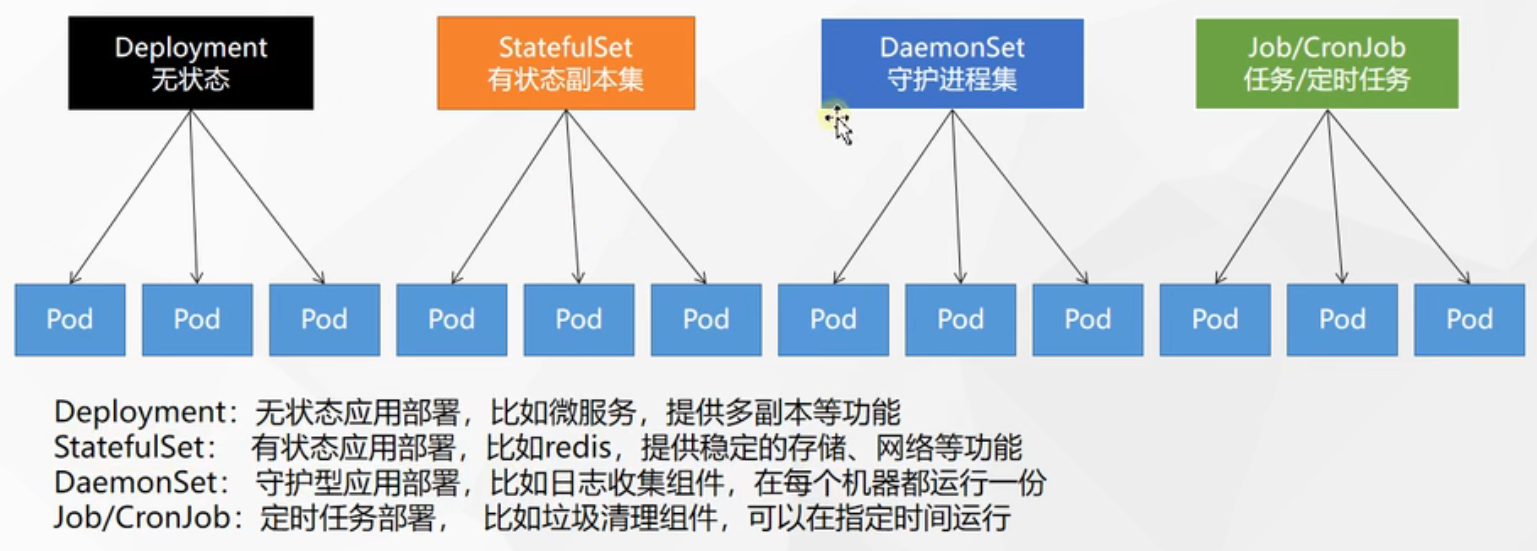
NAME:k8s 集群中资源对象的名称,区分大小写。如果不指定名称,系统则返回属于 TYPE 的全部资源对象列表
flags:kubectl 子命令的可选参数
kubectl 每个子命令(如 create、get、describe、delete 等)还有特定的 flags 参数,可以通过
kubectl [command] --help kubectl [command] [TYPE] --help1
2命令查看。
# Namespace
Namespace 默认只隔离资源,不隔离网络。语法格式:
kubectl [command] ns [NAME] [flags]
kubectl [command] ns --help
2
示例:
kubectl get ns
kubectl create ns namespace_name
kubectl delete ns namespace_name
# 查看已存在命名空间的yaml配置
kubectl get ns namespace_name -o=yaml
# 导出已存在命名空间的yaml配置
kubectl get ns namespace_name -o=yaml > namespace.yaml
# 查看不存在命名空间的yaml配置
kubectl create ns namespace_name -o=yaml --dry-run=client
# 导出不存在命名空间的yaml配置
kubectl create ns namespace_name -o=yaml --dry-run=client > namespace.yaml
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
# Pod
Pod 运行中的一组容器,Pod是kubernetes的最小单位。
一个pod中可以部署多个container,同一个pod的container共享网络空间。
语法格式:
kubectl [command] pod [NAME] [flags]
kubectl [command] pod --help
2
示例:
# 查看所有命名空间的pod
kubectl get pod -A
# 查看默认名称空间下的pod
kubectl get pod
# 查看指定名称空间下的pod
kubectl get pod -n namespace
# 查看默认名称空间下的pod(显示更加详细的信息)
kubectl get pod -owide
# 监听pod的变化
kubectl get pod -w
# Create and run a particular image in a pod.
kubectl run my-pod-nginx --image=docker.io/nginx:1.23 --port=80
kubectl run my-pod-tomcat --image=docker.io/tomcat --port=8080
# Show details of a specific resource or group of resources.
kubectl describe pod pod_name
kubectl describe pod pod_name -n nameapace
# Print the logs for a container in a pod or specified resource. If the pod has only one container, the container name is optional.
kubectl logs pod_name
# Execute a command in a container.
# kubectl exec (POD | TYPE/NAME) [-c CONTAINER] [flags] -- COMMAND [args...]
kubectl exec -it pod_name -- /bin/bash
kubectl delete pod pod_name
kubectl delete -n default pod pod_name
# 查看已存在pod的yaml配置
kubectl get pod my-pod-nginx -o=yaml
# 导出已存在pod的yaml配置
kubectl get pod my-pod-nginx -o=yaml > pod.yaml
# 查看不存在pod的yaml配置
kubectl run my-pod-nginx --image=docker.io/nginx:1.23 --port=80 -o=yaml --dry-run=client
# 导出不存在pod的yaml配置
kubectl run my-pod-nginx --image=docker.io/nginx:1.23 --port=80 -o=yaml --dry-run=client > pod.yaml
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
# Deployment
Deployment 控制 Pod,使Pod拥有多个副本,自愈、扩容等功能。
语法格式:
kubectl [command] deploy [NAME] [flags]
kubectl [command] deploy --help
2
示例:
kubectl get deployment
kubectl create deployment my-deploy-nginx --image=docker.io/nginx:1.23
kubectl create deployment my-deploy-nginx --image=docker.io/nginx:1.23 --replicas=2
kubectl expose deployment my-deploy-nginx --target-port=80 --port=10080 --type=NodePort --name my-deploy-nginx-svc
kubectl edit deployment my-deploy-nginx
# 扩容
kubectl scale --current-replicas=2 --replicas=3 deployment/my-deploy-nginx
# 缩容
kubectl scale --current-replicas=3 --replicas=2 deployment/my-deploy-nginx
# 滚动更新/不停机维护
kubectl set image deployment/my-deploy-nginx nginx=nginx:1.9.1 --record
# 查看历史记录
kubectl rollout history deployment/my-deploy-nginx
# 版本回退
kubectl rollout undo deployment/my-deploy-nginx --to-revision=1
kubectl delete deployment my-deploy-nginx
kubectl delete -n default deployment my-deploy-nginx
kubectl get deployment my-deploy-nginx -o=yaml
kubectl get deployment my-deploy-nginx -o=yaml > deployment.yaml
kubectl create deployment my-deploy-nginx --image=docker.io/nginx:1.23 --replicas=2 -o=yaml --dry-run=client > deployment.yaml
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
# Service
Service ,将一组Pods公开为网络服务的抽象方法,Pod的服务发现和负载均衡。
# Expose a resource as a new Kubernetes service.
# type: Type for this service: ClusterIP, NodePort, LoadBalancer, or ExternalName. Default is 'ClusterIP'.
# --type=ClusterIP: 仅仅集群内访问
# --type=NodePort: 集群外可以访问
# --port: The port that the service should serve on.
# --target-port: Name or number for the port on the container that the service should direct traffic to
kubectl expose pod my-pod-nginx --target-port=80 --port=10080 --type=NodePort --name my-pod-nginx-svc
kubectl expose pod my-pod-tomcat --target-port=8080 --port=18080 --type=NodePort --name my-pod-tomcat-svc
# 查看已存在svc的yaml配置
kubectl get svc my-pod-nginx -o=yaml
# 导出已存在svc的yaml配置
kubectl get svc my-pod-nginx -o=yaml > service.yaml
# 查看不存在svc的yaml配置
kubectl expose pod my-pod-nginx --target-port=80 --port=10080 --type=NodePort --name my-pod-nginx-svc -o=yaml --dry-run=client
# 导出不存在svc的yaml配置
kubectl expose pod my-pod-nginx --target-port=80 --port=10080 --type=NodePort --name my-pod-nginx-svc -o=yaml --dry-run=client > service.yaml
kubectl get service
kubectl get svc
kubectl delete svc my-pod-nginx
kubectl delete -n default service my-pod-nginx
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
# Ingress
Ingress用于实现用域名访问k8s内部应用。
https://kubernetes.github.io/ingress-nginx/deploy/ (opens new window)
minikube addons enable ingress
# YAML
kubectl apply -f xxx.yaml
kubectl delete -f xxx.yaml
2
# Example
# 创建pod
kubectl run my-pod-nginx --image=docker.io/nginx:1.23 --port=80
kubectl run my-pod-tomcat --image=docker.io/tomcat --port=8080
# 容器内访问
# 分别进入my-pod-nginx和my-pod-tomcat容器内部,执行如下命令:
curl localhost:80
curl localhost:8080
# 为pod创建svc
kubectl expose pod my-pod-nginx --target-port=80 --port=10080 --type=NodePort --name my-pod-nginx-svc
kubectl expose pod my-pod-tomcat --target-port=8080 --port=18080 --type=NodePort --name my-pod-tomcat-svc
# 查看svc
# 10080:37442/TCP,10080用于集群内访问,37442用于集群外访问
[k8s@k8s ~]$ kubectl get svc
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
kubernetes ClusterIP 10.96.0.1 <none> 443/TCP 53d
my-pod-nginx-svc NodePort 10.100.244.81 <none> 10080:37442/TCP 104s
my-pod-tomcat-svc NodePort 10.103.126.25 <none> 18080:58008/TCP 2s
# 集群内访问
# 在pod中可以通过serviceIp:port或者serviceName.namespace.svc:port访问其他pod
# 进入my-pod-nginx容器内部,访问tomcat
curl my-pod-tomcat-svc.default.svc:18080
# 进入my-pod-tomcat容器内部,访问nginx
curl my-pod-nginx-svc.default.svc:10080
# 集群外访问(在宿主机中)
[k8s@k8s ~]$ minikube ip
192.168.49.2
[k8s@k8s ~]$ curl 192.168.49.2:37442
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Welcome to nginx!</title>
<style>
html { color-scheme: light dark; }
body { width: 35em; margin: 0 auto;
font-family: Tahoma, Verdana, Arial, sans-serif; }
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Welcome to nginx!</h1>
<p>If you see this page, the nginx web server is successfully installed and
working. Further configuration is required.</p>
<p>For online documentation and support please refer to
<a href="http://nginx.org/">nginx.org</a>.<br/>
Commercial support is available at
<a href="http://nginx.com/">nginx.com</a>.</p>
<p><em>Thank you for using nginx.</em></p>
</body>
</html>
# 集群外访问(在浏览器中)
# https://kubernetes.io/docs/reference/generated/kubectl/kubectl-commands#port-forward
# Forward one or more local ports to a pod.
# kubectl port-forward TYPE/NAME [options] [LOCAL_PORT:]REMOTE_PORT [...[LOCAL_PORT_N:]REMOTE_PORT_N]
# Listen on port 37442 on all addresses, forwarding to 80 in the pod. Press Ctrl+C to end port exposure. Enter in the browser address bar http://192.168.1.26:37442/
kubectl port-forward --address 0.0.0.0 pod/my-pod-nginx 37442:80
kubectl port-forward --address 0.0.0.0 pod/my-pod-tomcat 58008:8080
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
# Q&A
# Service类型
ClusterIP(集群IP):在集群内使用,也是默认值。
ExternalName(外部名称):将 Service 映射到 DNS 名称
apiVersion: v1 kind: Service metadata: name: my-service spec: type: ExternalName externalName: my.database.example.com1
2
3
4
5
6
7LoadBalancer(负载均衡器)
NodePort(节点端口):在集群外可以访问,有效的端口号范围是 30000-32767。
如果不够的话,可以通过如下命令进行扩展:
minikube start --extra-config=apiserver.service-node-port-range=1-655351apiVersion: v1 kind: Service metadata: name: my-frontend-service spec: type: NodePort selector: app: web ports: - name: http protocol: TCP port: 80 targetPort: 8080 nodePort: 30000 # 30000-32767, Optional field1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
# Pod三种探针
StartupProbe:k8s 1.16版本后新加的探测方式,用于判断容器内应用程序是否已经启动。如果配置了startupProbe,就会先禁止其他的探测,直到它成功为止,成功后将不再进行探测。比较适用于容器启动时间长的场景。若没有配置该探针,默认就是success。
LivenessProbe:用于探测容器是否运行,如果探测失败,kubelet会根据配置的重启策略进行相应的处理。若没有配置该探针,默认就是success。
ReadinessProbe:一般用于探测容器内的程序是否健康,它的返回值如果为success,那么就代表这个容器已经完成启动,并且程序已经是可以接受流量的状态。
startupProbe:
# 指定探针探测方式为HTTPGetAction。
httpGet:
path: /api/healthcheck
port: 8080
livenessProbe:
httpGet:
path: /api/healthcheck
port: 8080
initialDelaySeconds: 3
periodSeconds: 3
readinessProbe:
httpGet:
path: /api/healthcheck
port: 8080
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
探针的探测方式:
- ExecAction:在容器内执行一个命令,如果返回值为0,则认为容器健康。
- TCPSocketAction:通过TCP连接检查容器内的端口是否通的,如果是通的就认为容器健康。
- HTTPGetAction:通过应用程序暴露的API地址检查程序是否正常,如果状态码为200~400之间,则认为容器健康。(常用)
探针的检查参数:
initialDelaySeconds: 60 # 初始化时间,指定探针多少秒后启动
timeoutSeconds: 2 # 超时时间
periodSeconds: 5 # 检测间隔,指定探针的探测周期
successThreshold: 1 # 检查成功为1次表示就绪
failureThreshold: 2 # 检测失败2次表示未就绪
2
3
4
5
# 访问Tomcat出现404
进入容器内部,ls 查看文件夹,发现有个空的webapps,但是有另外一个webapp.dist里面有相关的文件,将webapp.dist的文件拷贝过来即可。
cp -r webapps.dist/* ./webapps
# 修改Nginx首页
进入容器内部,执行
echo "111" > /usr/share/nginx/html/index.html
# Links
云原生Java架构师的第一课K8s+Docker+KubeSphere+DevOps (opens new window)
(2022版)最新、最全、最详细的Kubernetes(K8s)教程,从K8s安装到实战一套搞定 (opens new window)
